Introduction
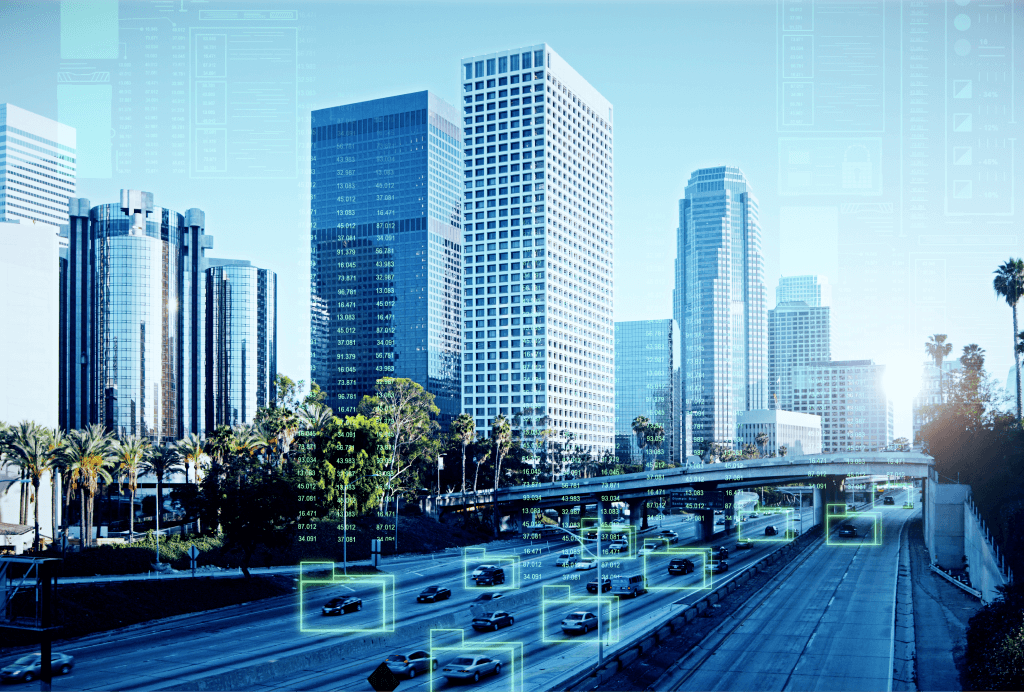
Smart camera technology has become a cornerstone of modern surveillance, offering advanced features like facial recognition, behavior analytics, and real-time alerts. While these systems enhance security, they also raise ethical questions about privacy, data use, and potential misuse. This article examines the delicate balance between privacy and protection, exploring how smart camera technology can be implemented responsibly.
The Promise of Smart Camera Technology
- Enhanced Security
Smart cameras detect and respond to threats in real time, reducing crime rates and improving public safety. Features like AI powered object detection and behavioral analytics are revolutionizing security. - Improved Efficiency
These systems minimize the need for constant human monitoring, allowing organizations to allocate resources more effectively. Automated alerts ensure rapid responses to incidents.
Privacy Concerns in Smart Surveillance
- Mass Data Collection
Smart cameras collect vast amounts of data, often without explicit consent. This raises concerns about how data is stored, shared, and used. - Facial Recognition and Bias
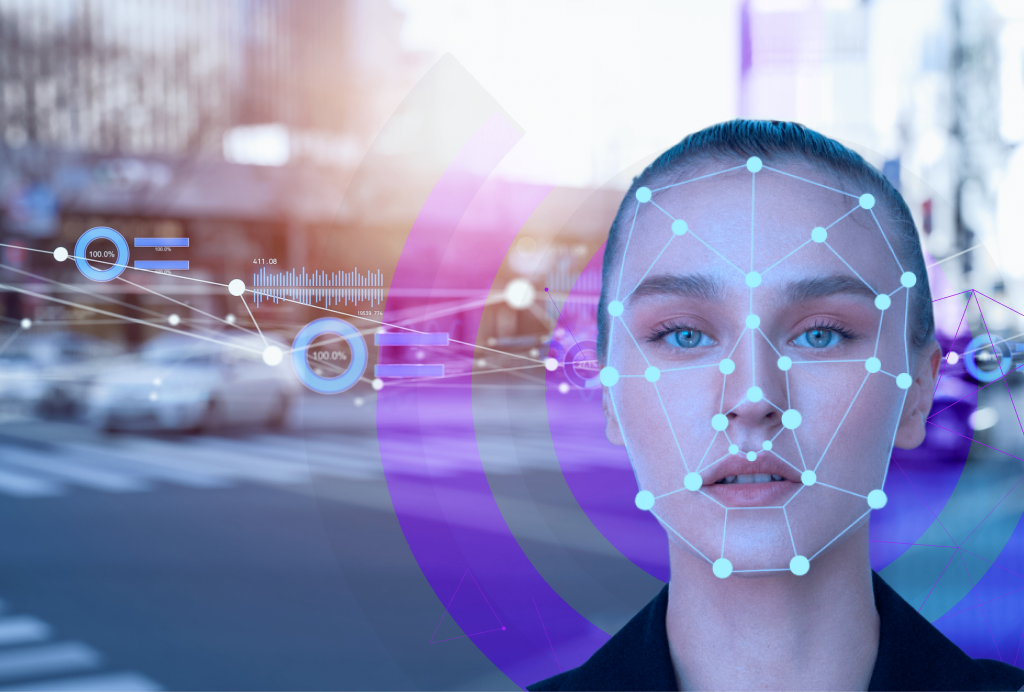
While facial recognition improves identification, it can lead to bias, inaccuracies, or discrimination. Ethical AI development is essential to address these issues. - Surveillance Overreach
Excessive surveillance can lead to a sense of invasion, especially in private or semi-private spaces, diminishing trust between communities and organizations.
Navigating the Ethical Challenges
- Transparency and Consent
Organizations must inform individuals about the use of surveillance systems and obtain consent when possible. Clear policies build trust and mitigate privacy concerns. - Data Security Measures
Implementing robust encryption and access controls ensures that sensitive data is protected from breaches or misuse. - Ethical AI Development
Ensuring AI algorithms are free from bias and regularly audited helps maintain fairness and accuracy in smart camera applications. - Regulations and Governance
Governments and organizations must collaborate to create regulations that balance security needs with privacy rights. Compliance with frameworks like GDPR can guide ethical implementation.
The Future of Ethical Surveillance
As technology evolves, the line between privacy and protection becomes increasingly blurred. The future of smart surveillance lies in finding a middle ground where security is enhanced without compromising individual freedoms. Through ethical design, transparent policies, and community engagement, smart cameras can achieve their full potential responsibly. We help smart cameras work as much as possible by providing new methods so that our smart cameras provide maximum security and also users’ rights are not violated.